Projects
Main menu:
Learning to Interact with a Human Partner
Mayada Oudah, Vahan Babushkin, Tennom Chenlinangjia, Ahmed Alshaer and Jacob Crandall
Nowadays, online learning is not yet widely implemented for Human-Robot Interaction due to a few difficulties imposed on algorithms. One of the issues is the random exploration technique required for efficient exploration of state space that results in unpredictable non-collaborative behavior. A slow convergence to the optimal solution is yet another issue. To overcome these two deficiencies, we introduce cheap-talk communication between user and robot that helps the online-learning algorithm to achieve effective collaboration between the two players. Read more...
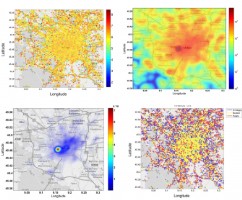
Misery Loves Company: Happiness and Communication in Cities
Aamena Alshamsi, Edmond Awad, Maryam Almehrezi, Vahan Babushkin, Pai-Ju Chang, Zakariyah Shoroye, Attila-Péter Tóth, Iyad Rahwan
Life in society would be impossible without communication between its members. People living in cities might appear to be in a more advantageous position in terms of availability of partners to communicate. To study a relationship between urban happiness and communications we consider Tweets and mobile communication intensity data from the city of Milan. Our analysis revealed that happy (unhappy) areas preferentially communicate with other areas of their type. The discovery of a sentiment-based homophily between different town districts potentially can be implemented in the redesigning of modern cities to improve the well-being of urban population. Read more...
Sensing Global Happiness, Diurnal Rhythms and Topics Through Social Media (Twitter)
Aamena Ali Al Shamsi, Vahan Babushkin, Vimitha Manohar
Social Media is a set of interactive applications and platforms for generating, sharing and exchanging information. It constantly becomes ubiquitous nowadays with emerging popular sites like Facebook and Twitter. Due to its popularity, Social Media can serve as an indicator of some human activities, emotions and interests that can reveal homophily patterns between areas, having some other parameters, totally irrelevant to Social Media, in common. In this project we analyze tweets from countries with a similar Human Development Index (HDI) to reveal how far this similarity affects user - generated content. Correlation between parameters inferred from Tweets and HDI can be used as a less expensive approach for obtaining different socioeconomic indices. Read more...
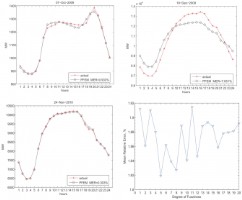
An Ensemble Model for Day-ahead Electricity Demand Time Series Forecasting
Wen Shen, Vahan Babushkin, Zeyar Aung, Wei Lee Woon
In the electrical power industry an accurate prediction of electricity demand or price is essential both for producers and suppliers. We consider the problem of day-ahead electricity demand prediction via the prism of Pattern Sequence-based Forecasting (PSF) algorithm, which predicts the future evolution of a time series based on the similarity of patterns. The proposed Pattern Forecasting Ensemble Model (PFEM) incorporates an ensemble of five PSF-style forecasting algorithms, namely the K-means (PSF itself), Self Organizing Map, Hierarchical Clustering, K-medoids and Fuzzy C-means. Iterating on weighted predicted values of these models allows to obtain superior results compared with all the other five individual components in terms of both MER and MAE. Read more...
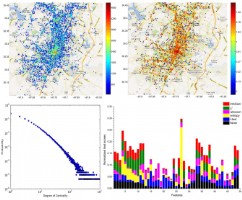
Inferring Social Relationships from Mobility Patterns of Location Based Online Social Networks Users
Vahan Babushkin
It is commonly accepted, that we tend to make social ties with people who live near us. However, it is not the case of online social networks’ users, whose friends can be living thousands kilometers away. Apart of making friends, location-based social networks (LBSN) allow their users to check-in in different locations. Those check-ins can be deployed to extract user’s mobility patterns, that can help us to study the regularity of users' movements and to discover friendship ties among them. We propose a method of predicting social relationships between members of LBSN using their mobility data. The potential application of this model can be found in friend recommendation systems. Read more...